A Comparison of DPWM and Inverter Loss Energy Based FCS-MPC for IPMSM
- Abstract
- Additional Comments
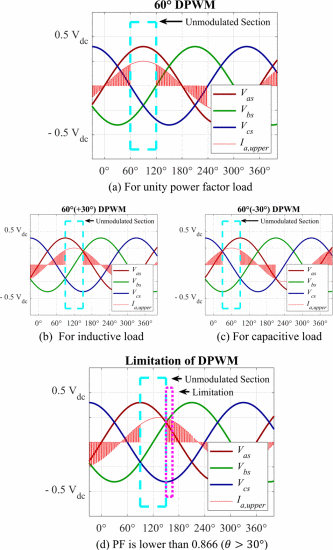
This paper presents a comparative analysis of a discontinuous pulse width modulation (DPWM) and a finite control set-model predictive control (FCS-MPC) when a power factor is lower than 0.866. An inverter loss energy-based algorithm, which has an objective to reduce inverter losses, is used in the FCS-MPC. Two control methods are implemented in an interior permanent magnet synchronous motor (IPMSM) based drive system. The simulation results lead to the conclusion that the FCS-MPC can achieve a better current total harmonic distortion (THDi) and a better inverter efficiency than the DPWM does when the power factor is lower than 0.866.