LLM-PPO Driver: Improving Autonomous Driving via LLM-Guided Reward Shaping and Imitation Learning
- Abstract
- Additional Comments
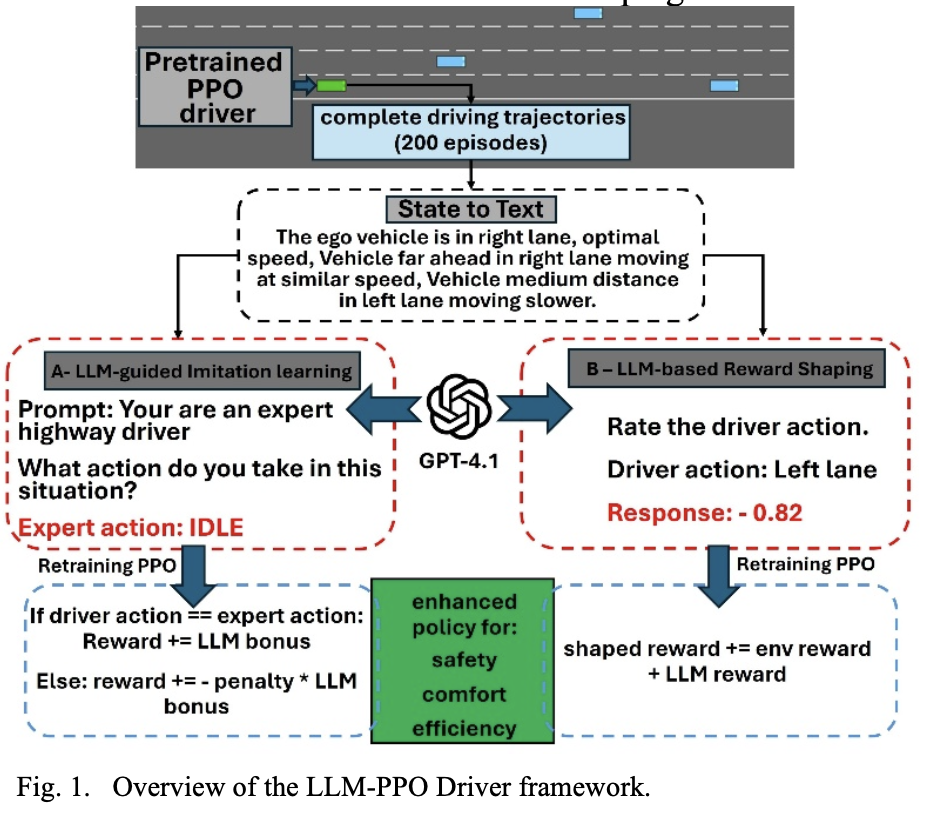
Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) has shown promise for autonomous driving; however, it suffers from sparse rewards, slow convergence, and unsafe behaviors due to exploration without prior knowledge. These limitations are particularly critical in safety-sensitive driving scenarios, where failure events are rare but severe. To address this issue, we propose LLM-PPO Driver, a framework that enhances PPO-based motion planning by incorporating high-level semantic driving knowledge from a Large Language Model (LLM). The LLM does not participate in real-time decision-making; instead, it provides structured prior knowledge that is integrated through reward shaping and imitation learning. This lightweight and modular design eliminates deployment-time inference overhead while guiding policy learning toward safer and more efficient behaviors. Experiments in the Gym highway-v0 environment demonstrate consistent improvements in task success and safety over a baseline PPO agent, with imitation learning yielding the largest performance gain. These results highlight the effectiveness of leveraging LLM-based prior knowledge to mitigate unsafe exploration and improve learning efficiency in autonomous driving.